
:::tip
关于借助Vue框架搭建Electron,有一个现成的解决方案,在这里,可惜的是Vue和Electron的版本有些老旧
:::
前期准备
全局安装 vue-cli
1 | yarn global add @vue/cli |
了解Electron的渲染进程与主进程。
新建一个Vue项目
借助 vue-cli 可以很方便的新建一个项目,这里可以借助其可视化工具来新建。
运行
1 | vue ui |
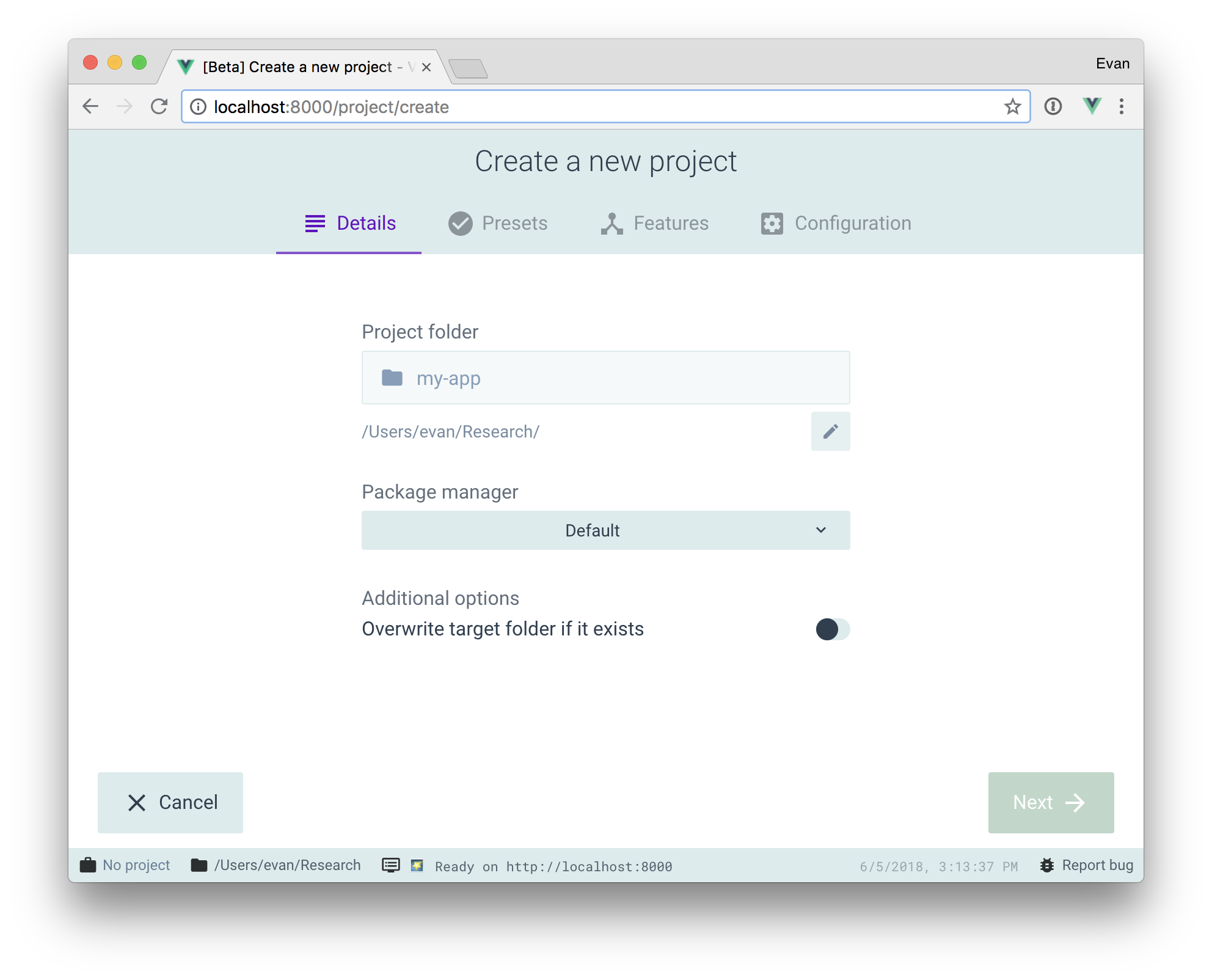
关于如何新建项目,这里不表,官方说明请戳这里
我选择的包管理是Yarn,构建工具是babel,使用webpack的童鞋也不必担心,原理相同,只是配置略有差别罢了。
对项目进行初始配置
假设你从来没有build过vue项目,那么现在,先运行:
1 | yarn run build |
不出意外的话,脚本会在你的项目目录中创建一个dist文件夹,现在,进到里面打开index.html,你会发现网页一片空白,浏览器报错说资源未找到。
打开index.html的源码,你会发现所有的资源引用都引用到根目录,本地打开则会索引到磁盘根目录下。这就非我们本意了。
1 |
|
为此,我们需要对项目进行一些简单的配置。
参照Vue官方配置说明,我们在项目根目录下建立一个vue.config.js文件,并在其中写入:
1 | module.exports={ |
现在再次build一下,你应该可以通过生成的index.html文件看到默认的网页了。
引入Electron
运行:
1 | yarn add electron --dev |
完成后,在项目根目录中建立main.js文件,并在其中写入:
1 | // Modules to control application life and create native browser window |
找到mainWindow.loadURL()这里,你能看到我注释了一个localhost的链接。由于我们这里只是简易搭建,就为了找找感觉,所以这里暂时不对开发环境和生产环境进行分别配置。
开发环境模拟
接上文,现在取消对localhost语句的注释,并把下面的url.format()那段语句注释掉,让我们来模拟开发环境吧。
首先,在package.json中的scripts中加上
==”electron”:”electron ./main.js”==
加上之后的scripts如下所示:
1 | "scripts": { |
这段语句的意思是,让electron从项目根目录下的main.js启动。
现在打开我们的命令行工具,开两个窗口。
第一个窗口输入:
1 | yarn run serve |
待到启动完成,在第二个窗口中输入
1 | yarn run electron |
不出意外的话,你就能看到弹出了一个窗口,里面就是你的网页。
同时,它还支持热更新,文件修改后就能及时得到反馈。
准备打包
光看显然不行,最终electron应用都是要打包的。
目前流行的electron打包工具有两种:
electron-builder
electron-packager
这里我们选用electron-builder。
运行:
1 | yarn add electron-builder --dev |
使用electron-builder,需要在package.json中添加如下内容:
1 | { |
图标是可选项,没有就不写
另外build中的productName最好与根层级的name同名,否则也可能出现构建失败的情况。
现在,基本上准备工作就做好了,现在可以开始写构建的脚本了。
在scripts中加入
==”electron-build”:”yarn build & electron-builder –dir”==
完成后的scripts如下:
1 | "scripts": { |
这段脚本的意思就是先将当前网页打包输出到 dist 文件夹中,再通过electron-builder对其进行打包,打包完成之后,会输出到当前项目目录下的build文件夹中 (此时生成的是一个文件夹,而不是安装包) 。
现在,打开终端,运行一下吧:
1 | yarn electron-build |
不出意外的话,打包会成功,然后进入到项目目录/build/win-unpacked,找到你的项目名.exe,双击运行,不报错就万事大吉了。
想打成安装包的话,修改脚本如下(针对自己的目标平台进行修改):
1 | { |
关于搭建Vue和Electron的简易混合开发环境的流程到这里就介绍完了。我折腾了一下午,踩了不少坑,但文中少有体现。有鉴于此,我觉得有必要把我的搭建过程写出来,让有相同需求的人少走弯路。
轉載來自 https://blog.richasy.cn/
- 本文标题:Vue 与 Electron 开发环境的简易搭建
- 创建时间:2019-05-11 20:45:12
- 本文链接:posts/5769.html
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!